Light multiplication for stable improvement of solar cells
By converting one high-energy light particle into two low energy particles, singlet fission makes high energy photons available for solar cells
Now that solar cells based on silicon technology have almost reached their efficiency limits, researchers from all over the world are looking for alternative technologies to further improve solar cell efficiency. Physicists from AMOLF and Cambridge University have used modelling techniques to compare two such promising technologies: singlet fission photon multipliers and tandem solar cells. While the potential efficiency improvement is almost equal, the singlet fission photon multiplier turned out to be more stable under varying weather conditions. Also, the singlet fission photon multiplier does not require modifications to the silicon technology, which means it could even be used to improve existing solar cells. The researchers publish their findings online in ACS Energy letters on 3 October 2018.
Over the last twenty years, the efficiency of high quality silicon solar cells increased only two percent and it will be very hard to make further improvements in the coming years. The main reason is that conventional solar cells waste a large part of the incoming sunlight. With silicon technology it is simply impossible to convert all sunlight into electrical energy because silicon only absorbs part of the solar spectrum. Also, high-energy photons from the blue part of the spectrum are not converted efficiently and they generate unwanted heat in the solar cell.
Alternative strategies
At research institute AMOLF, the Hybrid Solar Cells group led by Bruno Ehrler studies the properties of organic semiconductors to overcome the limitations of inorganic (silicon) solar cells. “There are two promising strategies that would improve solar cells tremendously”, says PhD student Moritz Futscher. “The first one, tandem solar cell technology based on a combination of hybrid perovskite materials and silicon, receives a lot of attention and is studied extensively by researchers from all over the world. We study perovskites as well, but we are also one of the few research groups that studies the second technology, which harnesses a process called singlet fission.”
Singlet fission
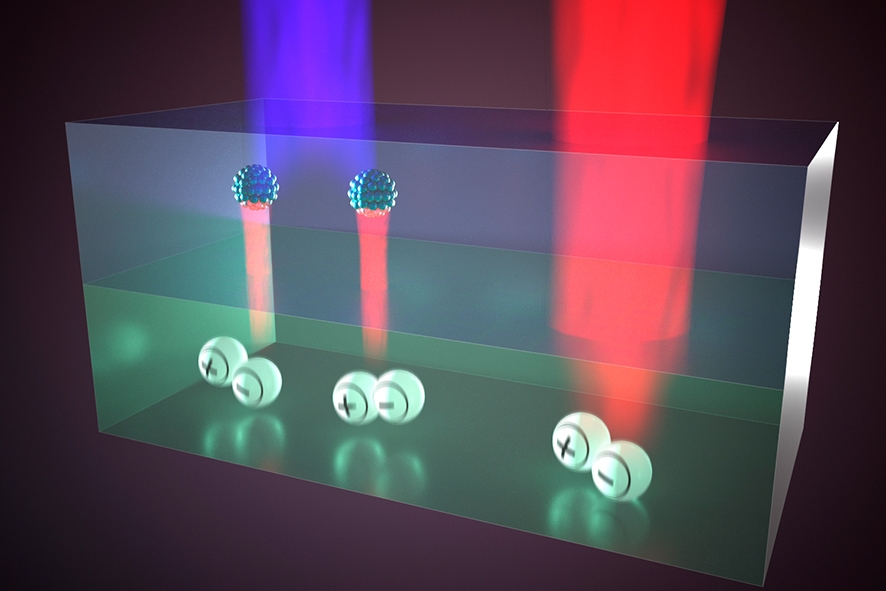
Singlet fission is a process occurring only in organic semiconductors. When a high-energy photon is absorbed, a high energy particle – called a singlet exciton – is generated. This singlet exciton converts into two triplet excitons that each have about half the energy of the singlet exciton. “With this approach we create two lower-energy photons out of one high-energy photon. These photons are then emitted into the underlying solar cell via quantum dots, tiny particles made from semiconductors”, Futscher explains. “This way, singlet fission serves as a photon multiplier.”
Theoretical comparison
Futscher and his colleagues theoretically compared singlet fission photon multipliers with tandem solar cells that use a combination of perovskites and silicon under real-weather conditions. “We know that tandem solar cells work very well in sunny regions but underperform in regions with fluctuating weather conditions. So, we took the weather and solar spectrum into account”, says Futscher. “We found that the combination of a singlet fission photon multiplier and silicon solar cells works just as well as the combination perovskites with silicon (tandem). However, under fluctuating weather conditions found in the Netherlands, the singlet fission photon multiplier proves the be a more stable choice.”
Easy improvement
The fact that singlet fission based solar cells potentially work as well as tandem solar cells – and even better under certain circumstances – makes it a very interesting alternative. “These photon multipliers are easy to make. It is basically a thin plastic foil that can be placed on top of an existing solar cell. The solar cell technology itself does not need to be changed,” says Futscher. “Although the technology works best with the latest state-of-the-art solar cells, such a singlet fission foil would even improve the performance of the silicon solar cells in use, especially under the varying weather conditions we face in the Netherlands.”
Image caption
The singlet fission photon multiplier converts high energy photons into two low energy photons, which can efficiently be transformed into electric energy by the solar cell. Without singlet fission, the high-energy light would lose a large part of its energy to heat. Credits image: Henk-Jan Boluijt
Reference
Moritz Hieronymus Futscher, Akshay Rao, and Bruno Ehrler, The Potential of Singlet Fission Photon Multipliers as an Alternative to Silicon-based Tandem Solar Cells,
ACS Energy Lett (september 26,2018) | DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.8b01322