Efficiency of silicon-based multijunction solar cells breaks 36% barrier
A team of researchers of the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Research (ISE, Freiburg) and AMOLF (Amsterdam) have fabricated a multijunction solar cell with an efficiency of 36.1%, the highest efficiency ever reached for a solar cell based on silicon. The team presented the new record at the European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference (PVSEC) in Lisbon on Thursday, September 21, 2023.
Limitations of silicon solar cells
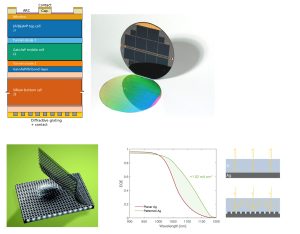
Solar cells and solar panels based on silicon are deployed allover the world at a very high rate, but their photovoltaic energy conversion efficiency is fundamentally limited to 29%. This limitation can be overcome by coating the solar cells with additional materials to create a “multijunction” solar cell. In such a geometry, multiple light absorption layers are stacked on top of each other, so that each layer effectively absorbs a specific part of the color spectrum of the light from the sun. This multi-layer concept can strongly enhance the cell efficiency.
New materials combined with new light management design
The new record combines a state-of-the-art “silicon TopCon” solar cell, a new high-efficiency cell design invented at Fraunhofer ISE, with two semiconductor layers composed of GaInP and GaInAsP that were also developed at Fraunhofer ISE. The layer stack is then coated with a specially designed metal/polymer nanocoating designed at AMOLF and fabricated jointly at AMOLF and Fraunhofer ISE. The backreflector improves the trapping of light inside the solar cell, so that the efficiency is for the first time improved beyond 36%.
Unique collaboration Fraunhofer ISE-AMOLF
Albert Polman, who led the AMOLF-part of the project. “This new record is the result of a unique collaboration between Fraunhofer ISE and AMOLF that started in 2020. The Fraunhofer team is world-renowned for the fabrication of ultra-high-efficiency solar cells based on Si and III-V semiconductors such as GaInP or GaAs. The AMOLF team has built up many years of experience in optimizing the management of light in solar cells. In this project, we brought this knowledge together, with this unique result. The solar cells have travelled between Freiburg and Amsterdam for the different processing steps, in this way building up the full solar cell.”
Frank Dimroth from Fraunhofer ISE adds: “It is a great achievement of the researchers in both teams to combine the best processes available to jointly realize a new record for the efficiency of Si based multijunction solar cell. Both, the new backreflector from AMOLF and the improved GaInAsP middle cell from Fraunhofer contributed to this outstanding result”.
New applications
The new ultrahigh-efficiency solar cells are currently more expensive to fabricate than conventional silicon solar cells, which have an efficiency up to 27%. However, the very high efficiency is a great benefit for applications where the available space is limited and a large amount of solar power must be generated within a small area. Applications are foreseen in solar-powered electric cars, consumer products, and drones, for example. The new light management design is also applicable in other types of solar cells, such as for example silicon-perovskite multijunction solar cells.
Publications
Optical solar cell design
Nano-patterned back-reflector with engineered near-field/far-field light scattering for enhanced light trapping in silicon-based multi-junction solar cells
A. Cordaro, R. Müller, S. Tabernig, N. Tucher, P. Schygulla, O. Höhn, B. Bläsi, and A. Polman, ArXiv2305.16462
Cell design, fabrication and characterization
Wafer-bonded two-terminal III-V//Si triple-junction solar cell with power conversion efficiency of 36.1 % at AM1.5g
P. Schygulla, R. Müller, O. Höhn, M. Schachtner, D. Chojniak, A. Cordaro, S. Tabernig, B. Bläsi, A. Polman, G. Siefer, D. Lackner, and F. Dimroth, submitted to Proc. EUPVSEC Conference, Lisbon, Progr. Photovolt. (2023)


